FFmpeg学习:音视频同步(1)相关基础定义
at 1年前 ca FFmpeg pv 1357 by touch
pts、dts、duration
time_base:时间基,所谓时间基表示的就是每个刻度是多少秒 ,例如
如果把1秒分为25等份,你可以理解就是一把尺,那么每一格表示的就是1/25秒。此时的time_base={1,25} ,
如果你是把1秒分成90000份,每一个刻度就是1/90000秒,此时的time_base={1,90000}。
在ffmpeg中。av_q2d(time_base)=每个刻度是多少秒
PTS:Presentation Time Stamp。PTS主要用于度量解码后的视频帧什么时候被显示出来,即显示时间戳,某一帧视频什么时候开始显示
pts的值就是占多少个时间刻度(占多少个格子)。它的单位不是秒,而是时间刻度。
DTS:Decode Time Stamp。DTS主要是标识读入内存中的帧数据流在什么时候开始送入解码器中进行解码,即解码时间戳
duration:某一帧视频显示持续时间,duration和pts单位一样,duration表示当前帧的持续时间占多少格。
不同结构体的 time_base
1、AVStream的time_base的单位是秒。每种格式的time_base的值不一样,根据采样来计算,比如mpeg的pts、dts都是以90kHz来采样的,所以采样间隔就是1/900000秒。
2、AVCodecContext的time_base单位同样为秒,不过精度没有AVStream->time_base高,大小为1/framerate。
3、AVPacket下的pts和dts以AVStream->time_base为单位(数值比较大),时间间隔就是AVStream->time_base。
4、AVFrame里面的pkt_pts和pkt_dts是拷贝自AVPacket,同样以AVStream->time_base为单位;而pts是为输出(显示)准备的,以AVCodecContex->time_base为单位。
5、输入流InputStream下的pts和dts以AV_TIME_BASE为单位(微秒),至于为什么要转化为微秒,可能是为了避免使用浮点数。
6、输出流OutputStream涉及音视频同步,结构和InputStream不同,暂时只作记录,不分析
三种时间基 tbr、tbn 和 tbc
不同的封装格式具有不同的时间基。在 FFmpeg 处理音视频过程中的不同阶段,也会采用不同的时间基。
FFmepg 中有三种时间基,命令行中 tbr、tbn 和 tbc 的打印值就是这三种时间基的倒数:
tbn:对应容器中的时间基。值是 AVStream.time_base 的倒数
tbc:对应编解码器中的时间基。值是 AVCodecContext.time_base 的倒数
tbr:从视频流中猜算得到,可能是帧率或场率(帧率的 2 倍)
内部时间基 AV_TIME_BASE
除以上三种时间基外,FFmpeg 还有一个内部时间基 AV_TIME_BASE(以及分数形式的 AV_TIME_BASE_Q)
// Internal time base represented as integer
#define AV_TIME_BASE 1000000
// Internal time base represented as fractional value
#define AV_TIME_BASE_Q (AVRational){1, AV_TIME_BASE}
//AV_TIME_BASE 及 AV_TIME_BASE_Q 用于 FFmpeg 内部函数处理,使用此时间基计算得到时间值表示的是微秒。时间基的转换,为什么要有时间基转换
首先,不同的封装格式,timebase是不一样的。另外,整个转码过程,不同的数据状态对应的时间基也不一致。
拿mpegts封装格式25fps来说(只说视频,音频大致一样,但也略有不同)。
非压缩时候的数据(即YUV或者其它),在ffmpeg中对应的结构体为AVFrame,它的时间基为AVCodecContext 的time_base ,AVRational{1,25}。
压缩后的数据(对应的结构体为AVPacket)对应的时间基为AVStream的time_base,AVRational{1,90000}。
因为数据状态不同,时间基不一样,所以我们必须转换,在1/25时间刻度下占10格,在1/90000下是占多少格。这就是pts的转换
时间基转换函数
av_rescale_q(int64_t a, AVRational bq, AVRational cq)函数
这个函数的作用是计算a*bq / cq来把时间戳从一个时间基调整到另外一个时间基。在进行时间基转换的时候,应该首先这个函数,因为它可以避免溢出的情况发生。
函数表示在bq下的占a个格子,在cq下是多少。
相关计算
一些时间基转换的场景
【计算视频总时长】
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx = NULL; avformat_open_input(&ifmt_ctx, filename, NULL, NULL); double totle_seconds = ifmt_ctx->duration * av_q2d(AV_TIME_BASE_Q);
【根据PTS求出一帧在视频中对应的秒数位置】
double sec = enc_pkt.pts * av_q2d(ofmt_ctx->streams[stream_index]->time_base);
【ffmpeg内部的时间戳与标准的时间转换方法】
timestamp(ffmpeg内部时间戳) = AV_TIME_BASE * time(秒) //其中 AV_TIME_BASE=1000000,其实就是将 单位 秒/s 转换成了 微秒/us time(秒) = AV_TIME_BASE_Q * timestamp(ffmpeg内部时间戳) //AV_TIME_BASE_Q=1/AV_TIME_BASE, 即(1微秒=1/1000000 秒)
【当需要把视频Seek到N秒的时候】
// 指定流索引 int pos = 20 * r2d(ic->streams[videoStream]->time_base); av_seek_frame(ic,videoStream, pos, AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD|AVSEEK_FLAG_FRAME ); // 未指定指定流索引 int64_t timestamp = N * AV_TIME_BASE; av_seek_frame(fmtctx, -1, timestamp, AVSEEK_FLAG_BACKWARD);
【关于音频pts的计算】
//音频sample_rate:samples per second,即采样率,表示每秒采集多少采样点。 //比如44100HZ,就是一秒采集44100个sample. 即每个sample的时间是1/44100秒 //一个音频帧的AVFrame有nb_samples个sample,所以一个AVFrame耗时是nb_samples\*(1/44100)秒,即标准时间下duration_s=nb_samples\*(1/44100)秒, //转换成AVStream时间基下 duration=duration_s / av_q2d(st->time_base) //即duration个时间基 //另外,st->time_base的num值一般等于采样率,所以duration=nb_samples. pts=n*duration=n*nb_samples
针对视频
I 帧/P 帧/B 帧
I 帧:I 帧(Intra-coded picture, 帧内编码帧,常称为关键帧)包含一幅完整的图像信息,属于帧内编码图像,不含运动矢量,在解码时不需要参考其他帧图像。因此在 I 帧图像处可以切换频道,而不会导致图像丢失或无法解码。I 帧图像用于阻止误差的累积和扩散。在闭合式 GOP 中,每个 GOP 的第一个帧一定是 I 帧,且当前 GOP 的数据不会参考前后 GOP 的数据。
P 帧:P 帧(Predictive-coded picture, 预测编码图像帧)是帧间编码帧,利用之前的 I 帧或 P 帧进行预测编码。
B 帧:B 帧(Bi-directionally predicted picture, 双向预测编码图像帧)是帧间编码帧,利用之前和(或)之后的 I 帧或 P 帧进行双向预测编码。B 帧不可以作为参考帧。
B 帧具有更高的压缩率,但需要更多的缓冲时间以及更高的 CPU 占用率,因此 B 帧适合本地存储以及视频点播,而不适用对实时性要求较高的直播系统。
解码和显示顺序
音频中 DTS 和 PTS 是相同的。视频中由于 B 帧需要双向预测,B 帧依赖于其前和其后的帧,因此含 B 帧的视频解码顺序与显示顺序不同,即 DTS 与 PTS 不同。当然,不含 B 帧的视频,其 DTS 和 PTS 是相同的。下图以一个开放式 GOP 示意图为例,说明视频流的解码顺序和显示顺序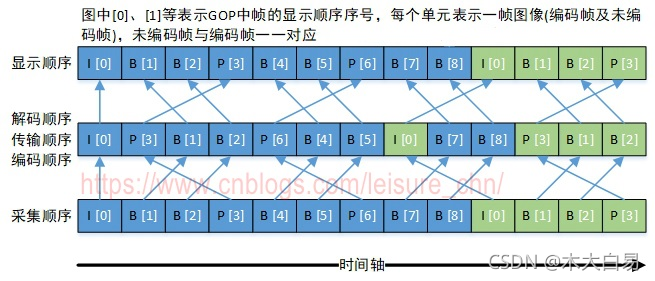
采集顺序指图像传感器采集原始信号得到图像帧的顺序。
编码顺序指编码器编码后图像帧的顺序。存储到磁盘的本地视频文件中图像帧的顺序与编码顺序相同。
传输顺序指编码后的流在网络中传输过程中图像帧的顺序。
解码顺序指解码器解码图像帧的顺序。
显示顺序指图像帧在显示器上显示的顺序。
采集顺序与显示顺序相同。编码顺序、传输顺序和解码顺序相同。
以图中“B[1]”帧为例进行说明,“B[1]”帧解码时需要参考“I[0]”帧和“P[3]”帧,因此“P[3]”帧必须比“B[1]”帧先解码。这就导致了解码顺序和显示顺序的不一致,后显示的帧需要先解码。
FFmpeg 具体相关API
时间值形式转换
av_q2d()将时间从 AVRational 形式转换为 double 形式。AVRational 是分数类型,double 是双精度浮点数类型,转换的结果单位是秒。转换前后的值基于同一时间基,仅仅是数值的表现形式不同而已。
av_q2d()实现如下:
/**
* Convert an AVRational to a `double`.
* @param a AVRational to convert
* @return `a` in floating-point form
* @see av_d2q()
*/
static inline double av_q2d(AVRational a){
return a.num / (double) a.den;
}av_q2d()使用方法如下:
AVStream stream; AVPacket packet; packet 播放时刻值:timestamp(单位秒) = packet.pts × av_q2d(stream.time_base); packet 播放时长值:duration(单位秒) = packet.duration × av_q2d(stream.time_base);
时间基转换函数
av_rescale_q()用于不同时间基的转换,用于将时间值从一种时间基转换为另一种时间基。
/** * Rescale a 64-bit integer by 2 rational numbers. * * The operation is mathematically equivalent to `a × bq / cq`. * * This function is equivalent to av_rescale_q_rnd() with #AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF. * * @see av_rescale(), av_rescale_rnd(), av_rescale_q_rnd() */ int64_t av_rescale_q(int64_t a, AVRational bq, AVRational cq) av_const;
av_packet_rescale_ts()用于将 AVPacket 中各种时间值从一种时间基转换为另一种时间基。
/** * Convert valid timing fields (timestamps / durations) in a packet from one * timebase to another. Timestamps with unknown values (AV_NOPTS_VALUE) will be * ignored. * * @param pkt packet on which the conversion will be performed * @param tb_src source timebase, in which the timing fields in pkt are * expressed * @param tb_dst destination timebase, to which the timing fields will be * converted */ void av_packet_rescale_ts(AVPacket *pkt, AVRational tb_src, AVRational tb_dst);
转封装过程中的时间基转换
容器中的时间基(AVStream.time_base,即前面的 tbn)定义如下:
typedef struct AVStream {
......
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented.
*
* decoding: set by libavformat
* encoding: May be set by the caller before avformat_write_header() to
* provide a hint to the muxer about the desired timebase. In
* avformat_write_header(), the muxer will overwrite this field
* with the timebase that will actually be used for the timestamps
* written into the file (which may or may not be related to the
* user-provided one, depending on the format).
*/
AVRational time_base;
......
}AVStream.time_base 是 AVPacket 中 pts 和 dts 的时间单位,输入流与输出流中 time_base 按如下方式确定:
对于输入流:打开输入文件后,调用 avformat_find_stream_info()可获取到每个流中的 time_base
对于输出流:打开输出文件后,调用 avformat_write_header()可根据输出文件封装格式确定每个流的 time_base 并写入输出文件中
不同封装格式具有不同的时间基,在转封装(将一种封装格式转换为另一种封装格式)过程中,时间基转换相关代码如下:
av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt); pkt.pts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.pts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base, AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF|AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX); pkt.dts = av_rescale_q_rnd(pkt.dts, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base, AV_ROUND_NEAR_INF|AV_ROUND_PASS_MINMAX); pkt.duration = av_rescale_q(pkt.duration, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base);
下面的代码具有和上面代码相同的效果:
// 从输入文件中读取 packet av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &pkt); // 将 packet 中的各时间值从输入流封装格式时间基转换到输出流封装格式时间基 av_packet_rescale_ts(&pkt, in_stream->time_base, out_stream->time_base);
这里流里的时间基in_stream->time_base和out_stream->time_base,是容器中的时间基,就是前面的 tbn。
转码过程中的时间基转换
编解码器中的时间基(AVCodecContext.time_base,即前面的tbc)定义如下:
typedef struct AVCodecContext {
......
/**
* This is the fundamental unit of time (in seconds) in terms
* of which frame timestamps are represented. For fixed-fps content,
* timebase should be 1/framerate and timestamp increments should be
* identically 1.
* This often, but not always is the inverse of the frame rate or field rate
* for video. 1/time_base is not the average frame rate if the frame rate is not
* constant.
*
* Like containers, elementary streams also can store timestamps, 1/time_base
* is the unit in which these timestamps are specified.
* As example of such codec time base see ISO/IEC 14496-2:2001(E)
* vop_time_increment_resolution and fixed_vop_rate
* (fixed_vop_rate == 0 implies that it is different from the framerate)
*
* - encoding: MUST be set by user.
* - decoding: the use of this field for decoding is deprecated.
* Use framerate instead.
*/
AVRational time_base;
......
}上述注释指出,AVCodecContext.time_base 是帧率(视频帧)的倒数,每帧时间戳递增 1,那么 tbc 就等于帧率。编码过程中,应由用户设置好此参数。解码过程中,此参数已过时,建议直接使用帧率倒数用作时间基。
这里有一个问题:按照此处注释说明,帧率为 25 的视频流,tbc 理应为 25,但实际值却为 50,不知作何解释?是否 tbc 已经过时,不具参考意义?
根据注释中的建议,实际使用时,在视频解码过程中,我们不使用 AVCodecContext.time_base,而用帧率倒数作时间基,在视频编码过程中,我们将 AVCodecContext.time_base 设置为帧率的倒数。
视频流
视频按帧播放,所以解码后的原始视频帧时间基为 1/framerate。
视频解码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx; AVStream *in_stream; AVCodecContext *dec_ctx; AVPacket packet; AVFrame *frame; // 从输入文件中读取编码帧 av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &packet); // 时间基转换 int raw_video_time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->framerate); av_packet_rescale_ts(packet, in_stream->time_base, raw_video_time_base); // 解码 avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, packet) avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
视频编码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ofmt_ctx; AVStream *out_stream; AVCodecContext *dec_ctx; AVCodecContext *enc_ctx; AVPacket packet; AVFrame *frame; // 编码 avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame); avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, packet); // 时间基转换 packet.stream_index = out_stream_idx; enc_ctx->time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->framerate); av_packet_rescale_ts(&opacket, enc_ctx->time_base, out_stream->time_base); // 将编码帧写入输出媒体文件 av_interleaved_write_frame(o_fmt_ctx, &packet);
音频流
音频按采样点播放,所以解码后的原始音频帧时间基为 1/sample_rate
音频解码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ifmt_ctx; AVStream *in_stream; AVCodecContext *dec_ctx; AVPacket packet; AVFrame *frame; // 从输入文件中读取编码帧 av_read_frame(ifmt_ctx, &packet); // 时间基转换 int raw_audio_time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->sample_rate); av_packet_rescale_ts(packet, in_stream->time_base, raw_audio_time_base); // 解码 avcodec_send_packet(dec_ctx, packet) avcodec_receive_frame(dec_ctx, frame);
音频编码过程中的时间基转换处理:
AVFormatContext *ofmt_ctx; AVStream *out_stream; AVCodecContext *dec_ctx; AVCodecContext *enc_ctx; AVPacket packet; AVFrame *frame; // 编码 avcodec_send_frame(enc_ctx, frame); avcodec_receive_packet(enc_ctx, packet); // 时间基转换 packet.stream_index = out_stream_idx; enc_ctx->time_base = av_inv_q(dec_ctx->sample_rate); av_packet_rescale_ts(&opacket, enc_ctx->time_base, out_stream->time_base); // 将编码帧写入输出媒体文件 av_interleaved_write_frame(o_fmt_ctx, &packet);
【音视频时间戳比较函数】av_compare_ts()
【函数定义】
int av_compare_ts(int64_t ts_a, AVRational tb_a, int64_t ts_b, AVRational tb_b)
{
int64_t a = tb_a.num * (int64_t)tb_b.den;
int64_t b = tb_b.num * (int64_t)tb_a.den;
if ((FFABS(ts_a)|a|FFABS(ts_b)|b) <= INT_MAX)
return (ts_a*a > ts_b*b) - (ts_a*a < ts_b*b);
if (av_rescale_rnd(ts_a, a, b, AV_ROUND_DOWN) < ts_b)
return -1;
if (av_rescale_rnd(ts_b, b, a, AV_ROUND_DOWN) < ts_a)
return 1;
return 0;
}【参数分析】
ts_a:frame a的pts
tb_a:a对应的时间基
ts_b:frame b的pts
tb_b:b对应的时间基
【返回值】
如果a在b之前,返回 -1(即a先显示)
如果a在b之后,返回 1
如果位置相同,返回 0
参考
FFmpeg DTS、PTS和时间戳TIME_BASE详解
FFmpeg中的时间基(time_base), AV_TIME_BASE
理解ffmpeg中的pts,dts,time_base
版权声明
本文仅代表作者观点,不代表码农殇立场。
本文系作者授权码农殇发表,未经许可,不得转载。